Introduction to Electric Car Models, EV Maintenance, Safety, and Battery Management
Electric vehicles (EVs) are cars powered by electricity instead of gasoline. There are different types of EVs: Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) run only on electricity, Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) use both electricity and gas, and Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) combine a gas engine with an electric motor. EVs have been around since the 1800s, but modern technology has made them more efficient, affordable, and popular.
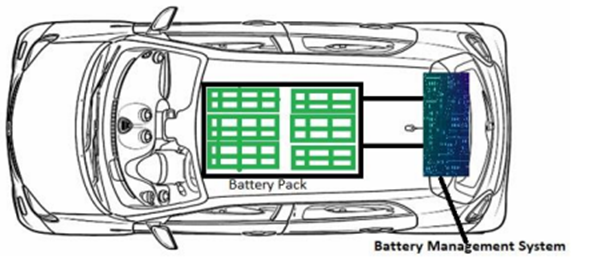
Understanding EV maintenance, safety, and battery management is crucial for owners. Proper care ensures the car runs smoothly, lasts longer, and stays safe. Recent advancements, like better battery technology and improved safety features, have made EVs more reliable. Battery management systems (BMS) play a key role in monitoring and protecting the battery, which is the most expensive part of an EV.
EVs also offer environmental and economic benefits. They produce fewer emissions, cost less to maintain, and can be powered by renewable energy. This article will cover popular EV models, maintenance tips, safety precautions, and battery management strategies.
Overview of Electric Car Models
- Tesla Model S: Known for its high performance, the Model S offers a long-range battery and advanced safety features like Autopilot.
- Nissan Leaf: This affordable and reliable EV is widely available and has a proven track record.
- Chevrolet Bolt EV: With a spacious interior and efficient battery, the Bolt is user-friendly and practical.
- BMW i3: Its lightweight design and innovative materials make it aerodynamic and eco-friendly.
- Audi e-tron: A luxury SUV with all-wheel drive and a high-tech infotainment system.
- Hyundai Kona Electric: Offers competitive pricing, fast charging, and excellent safety ratings.
- Ford Mustang Mach-E: Combines sporty design with versatile driving modes and advanced driver-assistance systems.
EV Maintenance: Key Points and Best Practices
- Battery Health Checks: Regularly monitor battery capacity and state of health to ensure longevity.
- Tire Maintenance: Proper tire pressure and alignment improve efficiency and safety.
- Brake System Care: Regenerative braking systems reduce wear but still need occasional inspection.
- Electrical System Checks: Inspect high-voltage components and connectors for damage.
- Software Updates: Firmware updates can enhance performance and fix bugs.
- Fluid Changes: EVs use fewer fluids, but coolant and brake fluid still need attention.
- Cleaning and Detailing: Use gentle products to avoid damaging sensitive components.
Electric Car Safety: Understanding the Risks and Precautions
- Fire Safety: Battery fires are rare but serious. Manufacturers use fire-resistant materials and cooling systems to prevent them.
- Collision Safety: EVs are designed with reinforced structures to protect occupants in crashes.
- Electrocution Risks: Safety features like automatic shutoffs prevent electric shocks during maintenance.
- Water Resistance: EVs are water-resistant, but avoid driving through deep floods.
- Emergency Response: First responders are trained to handle EV accidents safely.
- Cybersecurity: Protect your EV from hacking by using strong passwords and updating software.
- Child Safety: Teach children about the risks of silent operation and high-voltage components.
Battery Management: Strategies for Extending Battery Life and Performance
- Optimal Charging: Use Level 2 chargers and avoid fully discharging the battery.
- Temperature Management: Extreme heat or cold can reduce battery life. Park in shaded or insulated areas.
- Battery Health Monitoring: Use onboard diagnostics or apps to track battery health.
- Regenerative Braking: This feature recovers energy and extends battery life.
- Driving Habits: Smooth acceleration and braking reduce battery strain.
- Battery Replacement: Replacement costs vary, but warranties often cover 8-10 years.
- Recycling and Disposal: Recycling EV batteries reduces environmental impact.
Environmental and Economic Benefits of EVs
- Reduced Emissions: EVs produce fewer greenhouse gases, improving air quality.
- Energy Efficiency: EVs convert 77% of electrical energy to motion, compared to 12-30% for gas engines.
- Renewable Energy Integration: EVs can be charged using solar or wind power.
- Lower Operating Costs: EVs save money on fuel and maintenance.
- Government Incentives: Tax credits and rebates make EVs more affordable.
- Job Creation: The EV industry creates jobs in manufacturing, maintenance, and infrastructure.
- Future Trends: Advances in battery technology and charging infrastructure will make EVs even more accessible.



